How to operate a drone? It’s a question many ask, and the answer unfolds in a journey of understanding safety, navigation, and image capture. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of drone operation, from pre-flight checks to post-flight maintenance, equipping you with the knowledge to fly responsibly and capture stunning aerial footage. We’ll cover everything from understanding regulations and calibrating your drone’s systems to mastering advanced flight maneuvers and optimizing your camera settings for professional-quality results.
Prepare for takeoff!
Mastering drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical skill. This guide aims to bridge that gap, offering a structured approach to learning. By following the steps Artikeld, you’ll gain confidence in handling your drone and safely explore the exciting world of aerial photography and videography. Remember, safety and responsible operation are paramount throughout the entire process.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before embarking on any drone flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to strict safety procedures are paramount. This ensures both the safety of the drone and those in its vicinity. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents and damage.
Drone Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection involves systematically checking various drone components. This helps identify potential issues before takeoff, preventing mid-flight malfunctions.
| Component | Checkpoint | Component | Checkpoint |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Check for damage, cracks, or wear. Ensure they are securely fastened. | Battery | Verify battery level, check for any damage or swelling. Ensure proper connection. |
| Motors | Visually inspect for any damage or loose parts. Check for smooth rotation. | Camera | Check lens for smudges or obstructions. Confirm camera functionality. |
| Gimbal | Ensure the gimbal moves freely and is properly calibrated. | Airframe | Inspect for any cracks, dents, or damage to the drone’s body. |
| GPS | Confirm a strong GPS signal is acquired. | Radio Connection | Test the connection between the drone and the controller. |
Local Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Understanding and complying with local regulations and airspace restrictions is crucial for safe and legal drone operation. These regulations vary by location and may include restrictions on flight altitude, proximity to airports, and designated no-fly zones. Always check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations in your area.
Calculating Safe Flight Distances
Maintaining safe distances from obstacles and people is essential to prevent accidents. A simple method is to estimate the drone’s maximum range and keep it well within that limit. Always maintain visual line of sight with the drone, especially in areas with obstacles.
- Assess the environment for potential obstacles (buildings, trees, power lines).
- Determine the drone’s maximum range, considering wind conditions.
- Establish a safe distance buffer, at least 100 feet, from obstacles and people.
- Plan the flight path to maintain this safe distance throughout the flight.
Safe Flight Conditions Checklist
A decision-making flowchart helps determine if flight conditions are safe before initiating a flight. This involves considering various factors, including weather, wind speed, visibility, and airspace restrictions.
(A visual flowchart would be included here, detailing factors such as wind speed, visibility, GPS signal strength, battery level, and proximity to obstacles, leading to a “Safe to Fly” or “Unsafe to Fly” decision.)
Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding your drone’s controls and navigation systems is essential for safe and efficient operation. This section covers various aspects of controlling and navigating your drone.
Drone Controllers and Functionalities
Different drone controllers offer varying functionalities, from basic control over altitude and direction to advanced features such as waypoint navigation and camera control. Common features include joysticks for directional control, buttons for various functions (takeoff, landing, camera control), and a display screen showing telemetry data. More advanced controllers may integrate with mobile devices for enhanced control and real-time video streaming.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. A crucial aspect is learning the controls themselves, and for a comprehensive guide on this, I highly recommend checking out this resource on how to operate a drone which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Safe and responsible drone operation requires diligent study and practice, so take your time to master the fundamentals.
Compass and GPS Calibration
Proper calibration of the drone’s compass and GPS is crucial for accurate navigation and positioning. Calibration procedures typically involve performing specific maneuvers, such as rotating the drone or moving it in a figure-eight pattern, as instructed by the drone’s software. This ensures the drone accurately senses its orientation and location.
Interpreting Telemetry Data
Telemetry data provides real-time information about the drone’s status during flight. This includes battery level, signal strength, altitude, GPS coordinates, and more. Understanding this data allows for informed decision-making and helps prevent potential issues.
- Battery Level: Indicates remaining flight time.
- Signal Strength: Shows the strength of the connection between the drone and the controller.
- Altitude: Displays the drone’s height above ground level.
- GPS Coordinates: Shows the drone’s location.
Takeoff, Hovering, and Landing
Smooth takeoff, hovering, and landing are crucial for safe operation. These maneuvers require practice and a good understanding of the drone’s controls.
- Takeoff: Engage the throttle gently, allowing the drone to ascend slowly and steadily.
- Hovering: Maintain a stable altitude and position by adjusting the throttle and directional controls.
- Landing: Gradually lower the drone to the ground, reducing throttle smoothly until it touches down gently.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of autonomy and control. GPS mode relies on satellite signals for precise positioning, while attitude mode allows for more agile maneuvers but requires more pilot skill.
- GPS Mode: Provides stable flight, ideal for beginners and aerial photography.
- Attitude Mode: Offers more responsive control but requires greater pilot skill to maintain stability.
Flight Planning and Maneuvering
Careful flight planning and skillful maneuvering are essential for efficient and safe drone operation. This involves understanding various maneuvers and planning flight paths in advance.
Flight Path Planning
Planning flight paths before takeoff minimizes the risk of accidents and ensures efficient data collection. This involves identifying key points of interest, considering obstacles, and planning a route that avoids potential hazards.
Drone Maneuvers
Executing various maneuvers requires practice and a good understanding of the drone’s controls. Different maneuvers are used for different purposes, such as capturing specific angles or navigating complex environments.
| Maneuver | Description | Maneuver | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ascent | Increasing altitude. | Descent | Decreasing altitude. |
| Turn | Changing direction. | Yaw | Rotating the drone horizontally. |
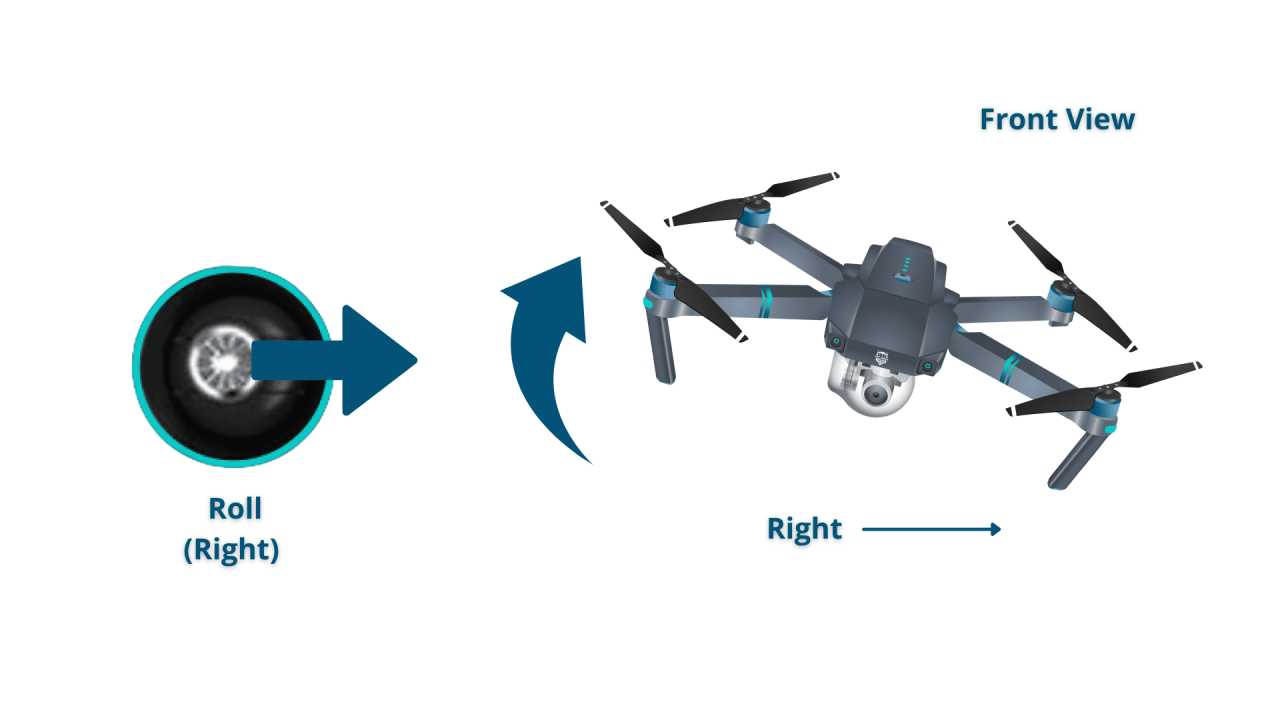
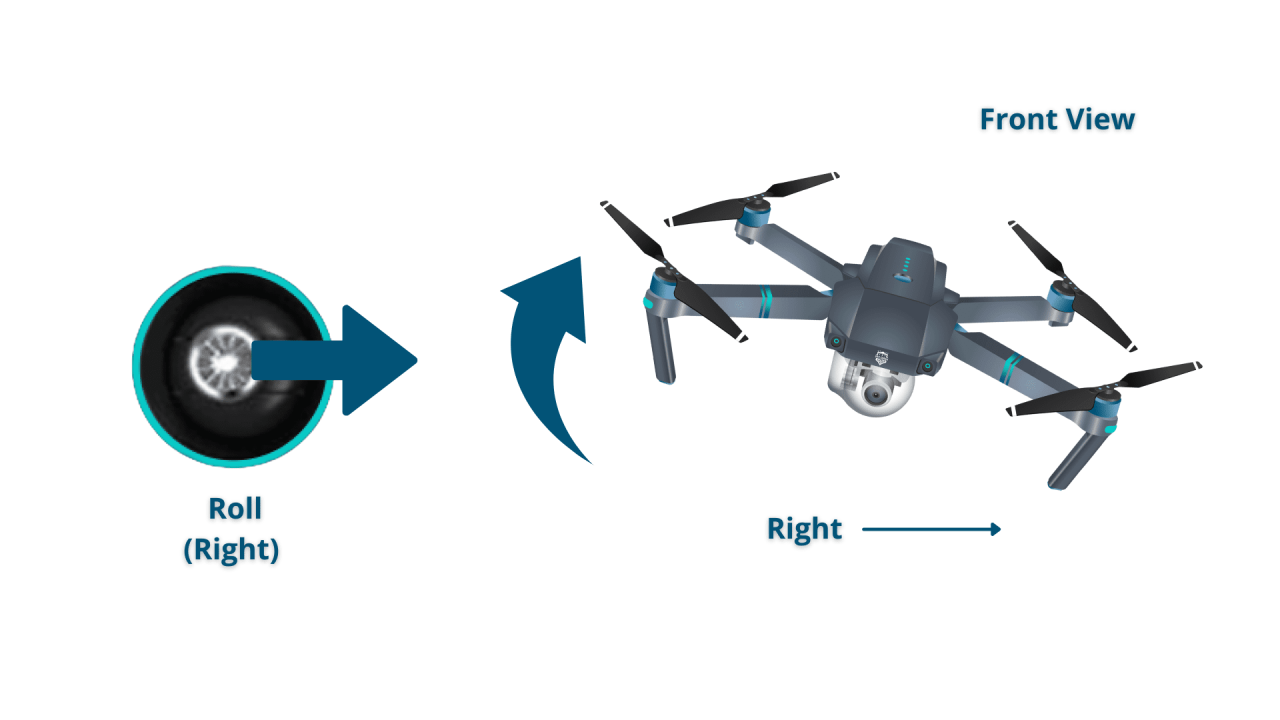
| Roll | Tilting the drone sideways. | Pitch | Tilting the drone forward or backward. |
Waypoint Navigation

Using waypoints allows for automated flight along a pre-defined path. This is particularly useful for tasks such as aerial mapping or surveying. Waypoints are typically set using the drone’s software or a dedicated flight planning application.
- Plan the flight path and mark the desired waypoints.
- Upload the waypoints to the drone.
- Initiate the automated flight sequence.
- Monitor the drone’s progress and make adjustments as needed.
Flying in Windy Conditions
Flying in windy conditions presents challenges due to increased instability and potential for the drone to be blown off course. Strategies for mitigating these challenges include reducing flight altitude, flying into the wind for take-off and landing, and using appropriate flight modes.
Sample Flight Plan
A sample flight plan for aerial photography of a building might involve establishing a safe distance from the building, planning a circular flight path around it at a consistent altitude, and using waypoints to ensure smooth and consistent coverage.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Understanding your drone camera’s settings and mastering image capture techniques are key to producing high-quality aerial photos and videos. This section covers various aspects of operating your drone camera.
Drone Camera Settings

Various camera settings affect image quality, including ISO, shutter speed, and aperture. Understanding how these settings interact allows for optimal image capture in various lighting conditions.
- ISO: Controls the camera’s sensitivity to light. Higher ISO values are better for low-light conditions, but can introduce noise.
- Shutter Speed: Determines how long the camera’s shutter remains open. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds can create motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the camera lens. A wider aperture (smaller f-number) allows more light, creating a shallower depth of field.
Adjusting Camera Settings for Lighting Conditions
Adjusting camera settings based on lighting conditions is essential for optimal image quality. In bright sunlight, you might use a faster shutter speed and lower ISO to avoid overexposure. In low light, you might increase the ISO and use a slower shutter speed, but be mindful of potential noise.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone , which offers comprehensive guidance. This initial understanding will significantly improve your drone piloting skills and ensure safe and responsible operation.
Taking High-Quality Photos and Videos
Capturing high-quality photos and videos involves careful composition, stable flight, and proper camera settings. Using appropriate flight modes, maintaining a steady hand, and planning your shots in advance are crucial for professional-looking results.
- Plan your shots carefully, considering composition and lighting.
- Maintain a steady flight to avoid blurry images.
- Use appropriate camera settings for the lighting conditions.
- Review your footage regularly to ensure quality.
Tips for Composing Shots
Effective composition techniques, such as the rule of thirds and leading lines, enhance visual storytelling. Understanding these principles improves the impact and aesthetics of your aerial footage.
Storing and Managing Drone Footage, How to operate a drone
Properly storing and managing drone footage ensures its longevity and accessibility. This involves using appropriate storage media, organizing files systematically, and backing up your data regularly.
- Use high-capacity SD cards for recording.
- Organize your files by date, location, and project.
- Regularly back up your footage to a cloud storage service or external hard drive.
Post-Flight Procedures and Maintenance
Following proper post-flight procedures and performing regular maintenance ensures the longevity and safety of your drone. This section details essential steps to take after each flight.
Powering Down and Storing the Drone
Properly powering down and storing the drone after a flight protects it from damage and extends its lifespan. This includes removing the battery, cleaning the drone, and storing it in a safe, dry place.
Cleaning and Inspecting the Drone
Regular cleaning and inspection for damage are crucial for maintaining the drone’s performance and preventing malfunctions. This involves checking for any damage to the propellers, motors, airframe, and other components.
Common Drone Maintenance Tasks
Performing regular maintenance tasks helps prevent potential issues and extends the drone’s lifespan. These tasks might include cleaning the propellers, checking for loose screws, lubricating moving parts, and calibrating the sensors.
Charging the Drone Battery Safely
Safe battery charging practices are essential to prevent damage and potential hazards. This involves using the appropriate charger, avoiding overcharging, and storing batteries properly.
Post-Flight Checklist
A post-flight checklist helps ensure that all necessary steps are taken after each flight. This checklist might include powering down the drone, removing the battery, inspecting for damage, cleaning the drone, and storing it safely.
(A visual checklist would be included here, outlining steps such as powering down the drone, removing the battery, inspecting for damage, cleaning the drone, and storing it safely.)
Troubleshooting Common Issues: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding common drone malfunctions and troubleshooting techniques helps resolve issues efficiently and ensures continued safe operation. This section provides guidance on diagnosing and resolving common problems.
Common Drone Malfunctions
Several common malfunctions can occur during drone operation. These include GPS signal loss, low battery, motor failure, and connectivity problems.
Troubleshooting Steps for Malfunctions
Troubleshooting steps vary depending on the specific malfunction. For example, GPS signal loss might be resolved by moving to an area with better signal reception, while a low battery requires charging.
Interpreting Error Messages
Understanding error messages displayed on the drone controller is crucial for diagnosing and resolving issues. These messages provide valuable clues about the nature of the problem.
Solutions for Connectivity Problems
Connectivity problems between the drone and controller can be resolved by checking for interference, ensuring proper antenna alignment, and restarting both devices.
Troubleshooting Flowchart
A troubleshooting flowchart can help users systematically diagnose and resolve drone issues. This flowchart would guide users through a series of questions and checks to pinpoint the source of the problem.
(A visual flowchart would be included here, guiding users through troubleshooting steps based on observed symptoms and error messages.)
Successfully operating a drone involves a careful balance of preparation, skill, and responsible decision-making. From meticulous pre-flight checks to mastering flight maneuvers and optimizing camera settings, each step contributes to a safe and rewarding flying experience. By understanding and applying the techniques discussed, you can confidently navigate the skies, capturing breathtaking aerial perspectives and producing high-quality visual content. Remember to always prioritize safety and adhere to local regulations for a positive and responsible drone experience.
FAQ Resource
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and automated features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with good stability and ease-of-use features.
How long does it take to learn to fly a drone?
The learning curve varies. Practice and understanding the fundamentals are key. Expect to spend several hours practicing before feeling comfortable with independent flight.
What happens if I lose the drone’s signal?
Most modern drones have return-to-home (RTH) functions. This feature automatically guides the drone back to its starting point if signal is lost. However, always maintain visual contact with your drone.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or if the drone experienced a significant impact.
What should I do if my drone malfunctions mid-flight?
Prioritize safety. If possible, attempt a controlled landing. If that’s not feasible, initiate the RTH function. Consult your drone’s manual for specific troubleshooting steps.